|
Computer Science - Mobile Device Operating Systems
Numerous manufacturers produce smartphones and tablets, but almost all of them run one of four mobile-friendly operating systems: Apple iOS, Android, Windows Phone, or BlackBerry OS. The majority of mobile operating system interfaces include icons and full-screen programmes that you access by tapping the touch-sensitive screen, in contrast to the majority of desktop and laptop operating system interfaces that have menus, windows, and icons that you access with a mouse. Mobile devices come with operating systems that are stored on nonvolatile memory, or memory that keeps its data even after the device is turned off. Although you can install updates, a mobile device comes with a specific OS that you cannot switch to. Despite the fact that the iPhone and iPad have different screen sizes, Apple iOS functions in the same way on both devices. iOS is exclusively available on Apple hardware; it cannot be used with any other hardware. Android For mobile devices, Google created the Android OS, a Linux derivative. The free and open source Android OS is used by many more affordable phones and tablets. Icons are arranged on a home screen in Android, which has a similar interface to iOS. The vast majority of iOS apps also have Android equivalents. Windows Phone As a version of Windows for mobile devices, Microsoft creates Windows Phone. Rectangular tiles on the Windows Phone main screen can be resized, and you can enlarge the tiles for the programmes you use the most. Fewer developers produce versions of their apps for Windows Phone because it has not gained the same level of popularity as iOS or Android. You can find the Windows Phone OS on a range of devices because Microsoft licences it to a number of different hardware producers. Current Windows-based tablets use Windows 10 Mobile, a mobile-friendly version of Windows 10 (note the name change from Phone to Mobile). Windows RT, a tablet version that was once offered, has been discontinued. BlackBerry Exclusive to BlackBerry smartphone hardware, the BlackBerry OS is a proprietary operating system. The BlackBerry OS will only receive a few updates, according to the parent company of the operating system; BlackBerry has lost market share in recent years and is not anticipated to be further developed.
0 Comments
 Computer Science- Devices for Mobile Computing Mobile devices are smaller and lighter than desktop and laptop computers since they are designed to be used on the go, as their name suggests. (Technically, laptops are mobile as well, but since they use desktop operating systems and offer comparable features, we discussed them with desktops.) Small touch-sensitive screens on handheld devices serve as both input and output mechanisms. Some modern gadgets, like the BlackBerry, still have integrated hardware keyboards, although most feature touchscreens with virtual keyboards that appear on-screen when needed. Tablets and smartphones are the two main categories of mobile devices now on the market. In the past, other types of devices (such digital music players, e-book readers, and personal organisers) were popular, but this popularity waned as smartphones and tablets improved. Smartphones Smartphones are more than just mobile phones; they are also tiny computers that provide you access to the Internet anywhere you are. By allowing you to copy and carry around data that you would often store on your PC, such as your address book, calendar, task lists, and so forth, they also aid in keeping you organised. You can play games, edit spreadsheets and text documents, read books, listen to music, and perform a variety of other computing functions on the majority of smartphones. We can divide smartphones into three groups based on operating systems: iPhones (iOS), Androids, and Windows Phones. We'll talk more about each of these groups later. Tablets A tablet is a touchscreen-equipped digital slate. It resembles an enormous smartphone, but most lack cell phone capabilities. (A tablet with cell phone functionality is referred to as a phablet.) A tablet bridges the gap between a laptop's processing capability and a smartphone's pocket-sized portability. The iPad, which runs on the same iOS operating system as the iPhone, is the most well-known tablet in the world. Other options include a number of tablets that run on Android, such the Samsung Galaxy Tab. The distinction between a laptop and a tablet is blurred by the detachable keyboard on Microsoft's Surface and Surface Pro tablets, leading some to refer to them as laplets. It's easiest to think of these as laptops that can pass for tablets because they still run the full workstation (desktop and laptop) version of Windows. Mobile Devices with a Specialty The catch with speciality mobile devices is that they frequently become well-liked for a single activity before smartphones and tablets and other more generic mobile devices, such as their hardware and apps, improve to the point where the typical user prefers using the app over carrying a different device. You can carry around the equivalent of a small library in your pocket thanks to e-book readers, which are essentially tablets designed just for reading e-books (like the Amazon Kindle or Barnes & Noble Nook). They offer wonderful features like long battery life and screens that don't fade in sunshine and create less eye strain. If crunching numbers is your thing, a modern scientific calculator packs more raw computing power than the earliest mainframes could fit into an index card-sized shell. There are calculators with video screens that let you graph complicated equations, but a smartphone app can also do this. Using tools with global positioning system (GPS) receivers, you can determine your precise location and get directions. Having a separate GPS device has become less desirable as more smartphones and cars now come equipped with GPS, making it easier to navigate roads and cities on foot or in a car. Some standalone GPS units have features that make them indispensable for endeavours like sailing or protracted backpacking trips. Computer Science - Chrome Os
For thin client systems—minimally equipped PCs made primarily for Internet use, as opposed to thick clients—Chrome OS is a Linux derivative created by Google. Because it cannot run desktop programmes like Microsoft Office, Chrome OS cannot serve as a viable alternative to a full-featured operating system like Microsoft Windows. Linux is a subset of UNIX, a much older operating system that was first deployed on servers as a command-line operating system. Since the operating system is free and open source, anyone can download it and alter the source code (if they know how to programme, of course). There are Linux variants available for practically every type of computer system.
The fundamental thing about open source software is that anyone can make changes and distribute this new version to the public. Open source software is typically free (you might have to pay to licence some software for business use). In contrast, a business or individual owns commercial software, such as Windows, and they are the only ones with the authority to create, alter, and sell it. A distribution, or distro, is a version of Linux that has been packed with utilities and add-ons appropriate for a certain use. The term "desktop environment" (DE) refers to the unique user interface that each distribution has. Ubuntu Linux is one of the most widely used computer operating systems, and you can download it for free online. The graphical interface for Ubuntu Linux is depicted in Figure 1-16. Although Chrome OS and other well-known operating systems are based on Linux, they often have their own distinctive user interfaces and many other changes. Python Programming Language - First Python Programme
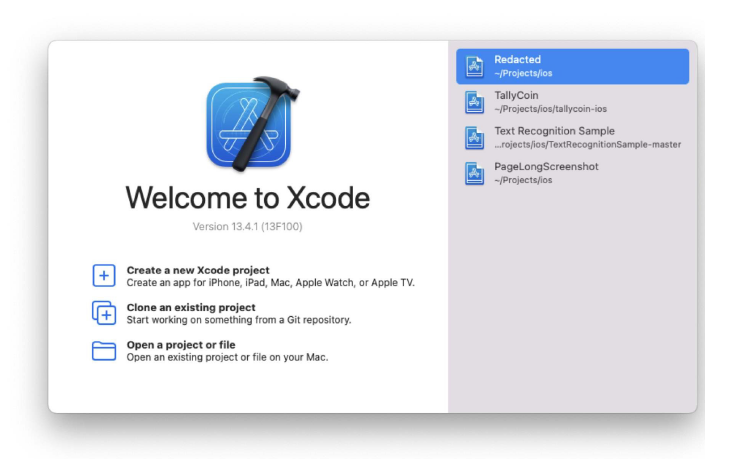
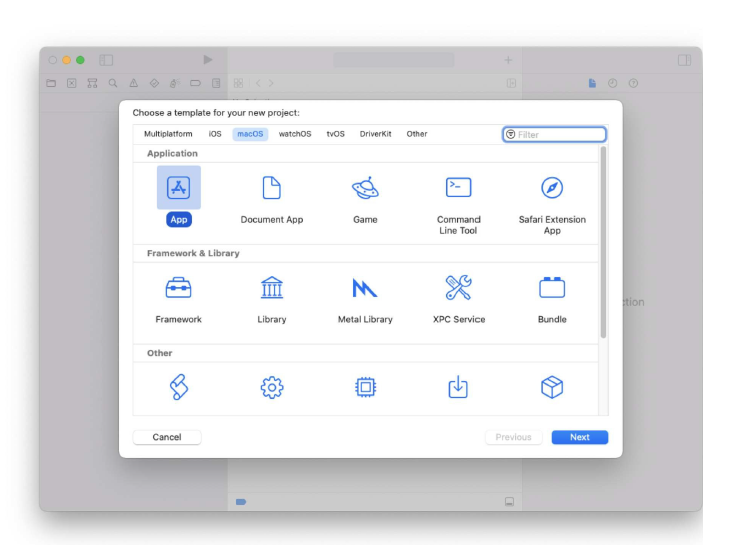
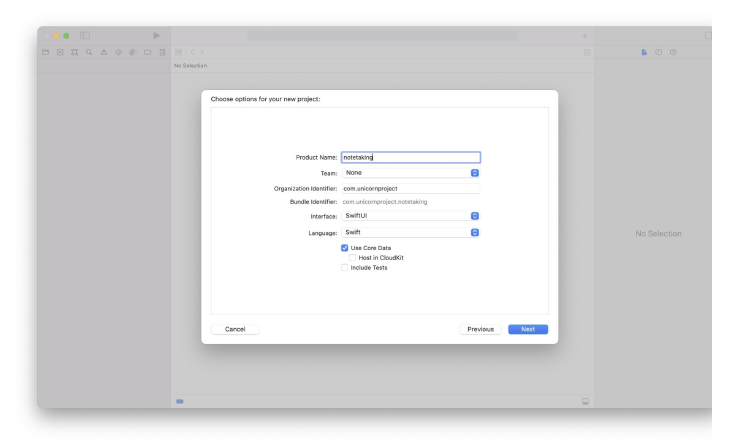
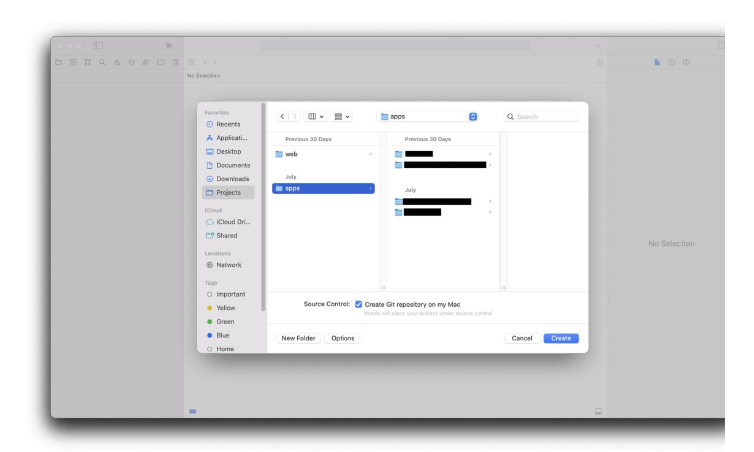
We will begin with a very basic first programme in order to understand the syntax of Python. When learning a new programming language, it is customary to begin with a Hello World application. "HELLO WORLD!" A script that prints "Hello World!" to the screen is all that a Hello World application is. This is especially easy to do in Python. "Hello World!" is printed. This is a Python one-liner, as you can see. To print a single text, we would need to design a fundamental structure in another language, complete with functions, classes, and more. However, let's investigate this situation. The so-called function with the name print is the first thing that stands out. When we utilise that function, a specific text is displayed on the screen. We must place the text we want to print between the brackets. The use of quote marks is another crucial component in this. They serve as a reminder that the text is a string and not the name of another object. A data type that represents text is a string. Without quotation marks, the interpreter will believe that Hello World! is a variable name rather than a text and will behave accordingly. Consequently, we will receive an error message. How to Build Iphone Apps - Creating MacOs App Project ( Step 3) Now that Xcode has been downloaded and installed on your Mac device, we can start building apps. Launch the Xcode programme. You have a few choices for starting a project on the left pane. The current tasks are displayed in the right pane. The right pan should be vacant if you are using Xcode for the first time. Let's select the Create a new Xcode project choice. Choose App under Application under macOS in the main menu. Type the product name here. In this instance, we'll just refer to it as notetaking. Keep Team set to None for the time being. We will discuss it afterward. Type the Organization Identifier here. Here, we'll use com.unicornproject as an illustration. You will observe the Bundle Identifier is formed as com.unicornproject.notetaking as you type it. This specific app's identification is provided by a Bundle Identifier. The organisation or person who created this initiative is identified by an Organization Identifier.Select Swift as the language and SwiftUI as the user interface. activating "Use Core Data" Later in the project , we will make use of this feature. then press Next. You can handle data object graphs in your application using the Core Data framework. It is commonly employed for storing local data. We must save the memo to the device in our note-taking app. Later, we'll delve even deeper into Core Data. If you are unsure whether your programme will use Core Data, you can also decide not to enable Core Data right away. You can still put it up if you discover it's necessary in the future. Select the directory where you want to save the file. Make sure Create Git repository on my Mac is turned on. The project will be established with an initialised git local repository. Let's save the note-taking project in this instance under the directory apps. To complete the project creation, click Create. For you, Xcode will produce a simple programme. To complete the project creation, click Create. For you, Xcode will produce a simple programme.
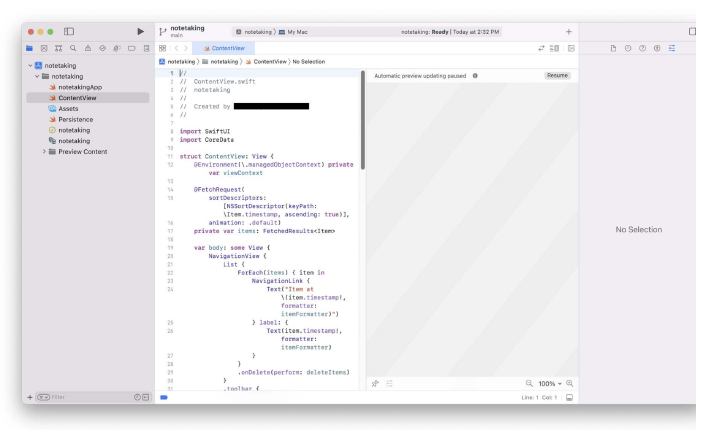
The code we have so far has now also been added to your local git history . How to Build Iphone Apps - A Note Taking App The first example, would be, we will learn how to build a note taking app. By creating this, we will become acquainted with:
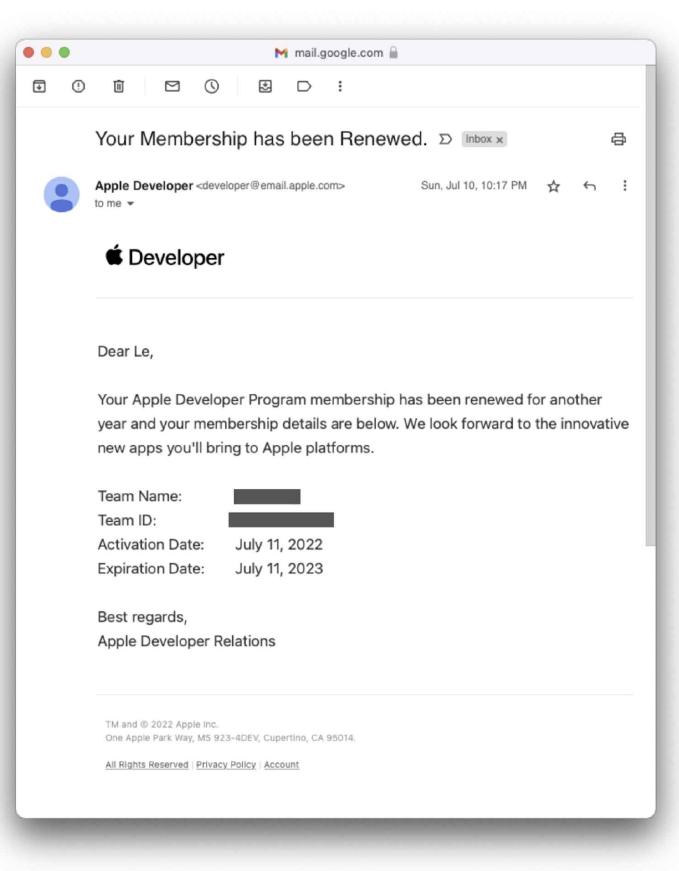
the basic procedure for producing a macOS app How to use local files with Core Data Principles of SwiftUI The following elements must be present in this note-taking app: The user can see every memo. The user may change any remark. Even after the programme closes, the note remains. How to Build Iphone Apps - Apple Developer Program Membership ( Step 3) We must sign up for the Apple Developer Program in order to create for macOS or iOS. Access to advanced app features, beta OS releases, and the tools required to create, test, and disseminate apps are all included with membership. It currently costs $99 a year for both people and businesses. You might be wondering if you still need to pay $99 right away if you're not ready to submit this app to the App Store. No, is the response. On a Mac, you can construct it. However, you must be enrolled in the programme once you are prepared to discharge. Do you know that for $99 a year, you can create numerous apps for both iOS and macOS? Even though this initial investment may seem high to some, if you intend to create numerous apps, you can benefit more from this programme. Click Enroll after visiting https://developer.apple.com/programs/. You can access the enrollment procedure there. After completing the sign-up procedure and paying the annual fee, you will get a confirmation email that looks something like this.
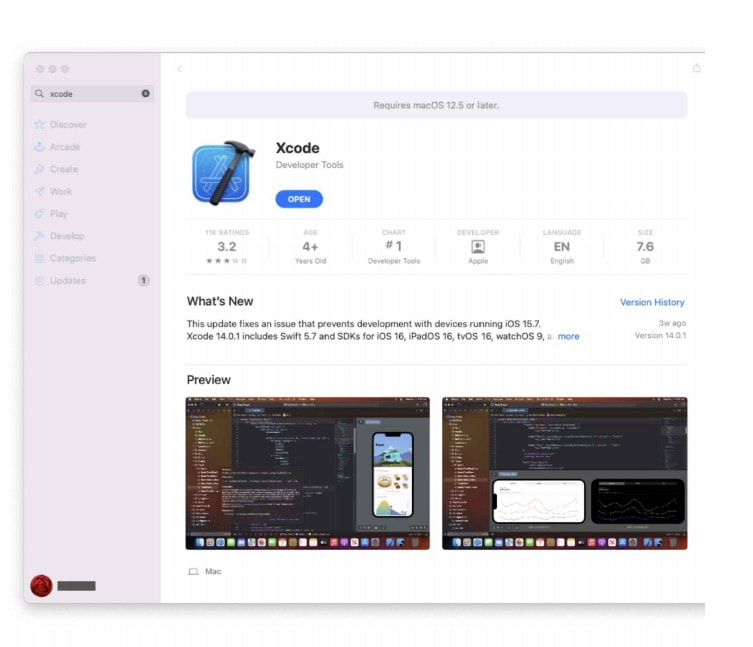
How to Build Iphone Apps - Install Xcode ( Step 2) On your Mac, launch the App Store and search for Xcode. Look up Xcode in the App Store. Xcode ought to appear in the search results. Select Get. Because Xcode has been loaded, the button in the aforementioned screenshot says "Open." It should say Get if you have never loaded Xcode. Given that Xcode is currently 7.6 GB in size, loading may take some time.
During the download and implementation, make sure your internet connection is stable. How to Build Iphone Apps-Introduction (step 1)
MAC Computer You can use an iMac, MacBook, or MacBook Air to create macOS apps. It makes no difference. However, more potent processors might be found in newer versions. You'll notice a significant decrease in build periods with them, leading to quicker Xcode development. |
AuthorAnything you need to know about computer science Archives
May 2023
Categories
All
|





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed