|
Candidiasis
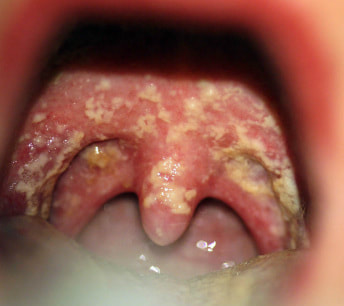
Candidiasis may be divided into cutaneous candidiasis, muco cutaneous candidiasis, and vulvovaginal candidiasis. Cutaneous candidiasis may present as rash such as rash on the skin fold of obese person or diaper rash. The rash is localized erythematous rash. Mucocutaneous candidiasis may present as creamy curdlike patches on the tongue or oral mucosa. The common example of mucocutaneous may include oropharyngeal candidiasis and oral thrush. Patient with AIDS may present with oral thrust. Vulvovaginal candidiasis may present with burning, itching, of the vulvovaginal with thick creamy white discharge from the vagina. Patient with AIDS may present with vulvovaginal candidiasis. Immunocompromised patient may present with disseminated candidiasis ( commonly individual with diabetes, intensive care unit patient, AIDS patient, cancer and chemotherapy taken patient). Defect of the T cell may present with severe infection of the skin and mucous membrane ( chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis ). Candidiasis is caused mostly by Candida albicans. The laboratory investigation may reveal the formation of the germ tubes in case of candida albicans. Direct microscopic examination may reveal the present of pseudohyphae and budding yeast. Impairment of the immune defenses may lead to candidiasis. The common treatment of candidiasis may include fluconazole, itraconazole, miconazole and amphotericin B.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Kembara's Health SolutionsDiscovering the world of health and medicine. Archives
June 2023
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed