|
Pneumococcal pneumonia
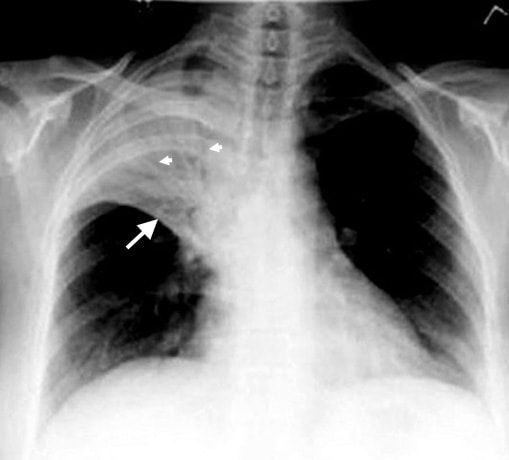
Pneumococcal pneumonia is caused by streptococcus pneumoniae. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram positive diplococci, sensitive to optochin and bile and alpha hemolytic. The virulence factors of streptococcus pneumoniae may include secretory IgA protease, antiphagocytic polysaccharides capsues, phosphorylcholine and pneumolysin. These virulence factors may promotes cellular invasion and inhibit phagocytic killing. The component of the cell wall such as teichoic acid and peptidoglycan may induce the inflammatory response to the host. The common mode of transmission is via respiratory droplets, organism aspiration from the oropharynx and due to direct contact. Patient with pneumococcal pneumonia may present with sudden onset of fever, shortness of breath, chills, bloody sputum and productive cough. Lobar pneumococcal pneumonia is the commonest form. There are over 80 serotypes of streptococcus pneumoniae based on the polysaccharide capsule. There is a conjugated vaccine against 7 serotypes and polyvalent vaccine against 23 serotypes of streptococcus pneumoniae. Streptococcus pneumoniae may also cause meningitis, otitis media and sinusitis. The treatments may include erythromycin, chloramphenicol and vancomycin.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Kembara's Health SolutionsDiscovering the world of health and medicine. Archives
June 2023
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed